INVERSE Korea
Project background
INVERSE-Korea is a scientific initiative endorsed by the World Meteorological Organization (WMO) as part of the Integrated Global Greenhouse Gas Information System (IG3IS). The project provides accurate, observation-based, and scientifically robust estimates of anthropogenic greenhouse gas (GHG) emissions — specifically carbon dioxide (CO₂), methane (CH₄), and sulfur hexafluoride (SF₆) — across the Korean Peninsula.
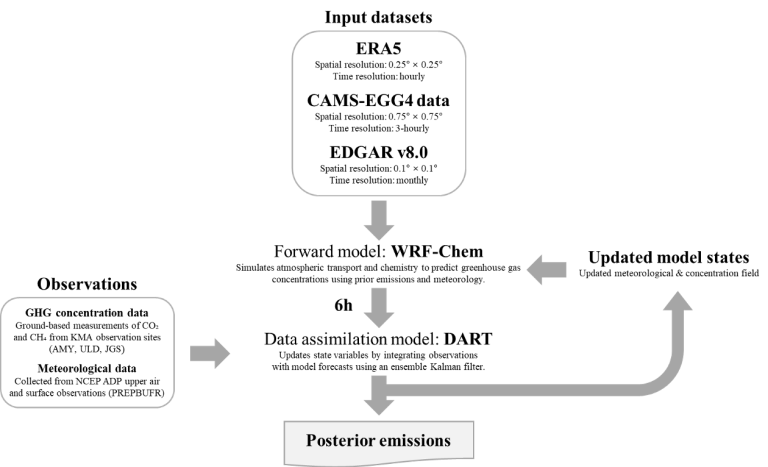
Named for its focus on inverse modelling, the project uses the Weather Research and Forecasting model with Chemistry (WRF-Chem) and the Data Assimilation Research Testbed (DART) to assess emissions.
Collaborative network
INVERSE-Korea is led by the Ecosystem–Atmosphere Process Laboratory at Yonsei University, in close collaboration with:
- National Institute of Meteorological Sciences (NIMS), Republic of Korea
- Korea Environment Institute (KEI)
- Emory University, Atlanta, United States of America
- Pohang University of Science and Technology (POSTECH)
- WMO Integrated Global Greenhouse Gas Information System (IG3IS)
Objectives
- Understand how variations in natural net greenhouse gas emissions are influenced by climate change.
- Reduce uncertainty in emissions of non-CO₂ gases such as CH₄, N₂O and fluorinated gases (F-gases).
- Identify missing or sporadic emission sources using top-down atmospheric inversion methods.
- Resolve discrepancies between national total emissions and aggregated data from local governments.
- Prioritize research to reduce emission uncertainties by comparing top-down and bottom-up approaches.
- Evaluate the impact of greenhouse gas reduction policies.
Outputs
Phase 0 (2012–2020)
- Global modelling system development (continental scale)
- CarbonTracker-Asia, based on the NOAA CarbonTracker (United States)
- Improvement of terrestrial ecosystem modelling
Phase 1 (2021–2023)
- System development for CO₂, CH₄ and SF₆ (city scale)
- Eulerian-based inversion system (WRF-Chem/DART, GEOS-Chem)
- Lagrangian-based inversion system (STILT, FLEXPART)
- Expansion of high-accuracy GHG concentration measurement network in the Republic of Korea
- Improved model physics for complex terrain
Phase 2 (2024–2026)
- System improvement and uncertainty quantification (city scale)
- Eulerian-based inversion system (WRF-Chem/DART)
- Lagrangian-based inversion system (FLEXINVERT)
- Satellite data analysis using high-resolution CH₄ remote-sensing data
Expected outcomes
- Improve understanding of emission inventories and reduce related uncertainties, especially for non-CO₂ greenhouse gases.
- Improve characterization of urban-scale emissions by integrating data from flux observations — such as eddy covariance measurements in the Seoul metropolitan area — and from tall-tower observations like the 555 m Lotte World Tower.
- Support national Measurement, Reporting and Verification (MRV) systems by providing independent validation of national and local emission inventories, essential for transparent climate reporting and policymaking.
Achievements
The multidisciplinary and international INVERSE-Korea team ensures scientific rigor, comprehensive data integration, and strong policy relevance.
Related links and documents:
- Ecosystem-Atmosphere Interaction Study - INVERSE-Korea
- Top-down estimates of CO2 and CH4 emissions in Korea based on an inverse modelling framework
- IG3IS Research Activity in Korea: From Eddy Covariance Measurement to Atmospheric Inversion (Presentation)
- IG3IS Research activity in Korea: From Eddy Covariance Measurement to Atmospheric Inversion on Vimeo (Recording)
